Why FIDO2 is More Secure Than TOTP: Understanding Phishing Protection
Introduction
Time-based One-Time Passwords (TOTP) have long been the standard for two-factor authentication, but they harbor a critical vulnerability: they are susceptible to phishing attacks. FIDO2 (Fast Identity Online 2), the modern authentication standard, eliminates this weakness through cryptographic origin binding. This article explores why FIDO2 represents a fundamental security improvement over TOTP.
The Fatal Flaw in TOTP
TOTP generates six-digit codes that refresh every 30 seconds. While this seems secure, these codes suffer from a fundamental problem: they can be used by any application (i.e. website) that gets the OTP. The codes themselves carry no information about where they should be used, making them bearer tokens—whoever presents the code can authenticate.
This creates a perfect opportunity for phishing attacks. If an attacker can trick a user into entering their TOTP code on a malicious site, that code can be immediately relayed to the legitimate service within the 30-second validity window.
The Evilginx Attack: How TOTP Phishing Works
Evilginx is a sophisticated phishing framework that demonstrates the vulnerability of TOTP and other traditional authentication methods. Here is how it operates:
Attack Flow Breakdown:
Initial Deception: The victim receives a convincing phishing email with a link to a domain that looks legitimate (e.g.,
googIe.cominstead ofgoogle.com)Transparent Proxy: Evilginx sits between the victim and the real website, acting as a reverse proxy that forwards all requests and responses
Credential Harvesting: When the user enters their username, password, and TOTP code, Evilginx captures everything while simultaneously forwarding it to the legitimate site
Session Hijacking: Most critically, Evilginx captures the session cookie returned by the legitimate site after successful authentication
Account Takeover: The attacker now has a valid session cookie and can access the account without needing to authenticate again
Why TOTP Cannot Defend Against This: The TOTP code is valid for the legitimate service, and the proxy simply relays it in real-time. The service cannot distinguish between the legitimate user and the attacker's proxy.
How FIDO2 Protects Against Phishing
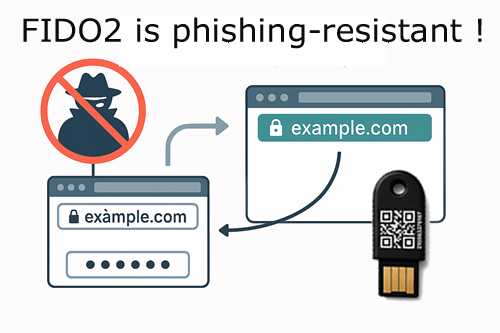
FIDO2 uses public key cryptography with a crucial security feature: cryptographic origin binding. This means every authentication is cryptographically tied to the specific domain where it was created.
FQDN Verification in FIDO2
When a FIDO2 authentication occurs, the domain name (Fully Qualified Domain Name or FQDN) is an integral part of the cryptographic challenge-response process:
Legitimate FIDO2 Authentication on google.com
What Happens During a Phishing Attempt with FIDO2:
FIDO2 Blocks Phishing Attack on googIe.com (fake)
Key Differences:
With TOTP (Vulnerable):
- User sees fake login page that looks real
- User enters TOTP code
123456 - Code is valid for
google.com - Proxy forwards code to real
google.com - Authentication succeeds, attacker wins
With FIDO2 (Protected):
- User sees fake login page
- Browser attempts FIDO2 authentication
- Authenticator checks: Is this
google.com? NO, it'sgoogIe.com - Authentication fails immediately
- User is alerted something is wrong
- Phishing attack prevented
Additional Security Advantages of FIDO2
1. No Shared Secrets
TOTP relies on a shared secret stored on both the server and the user's device. If the server is breached, these secrets can be stolen. FIDO2 uses asymmetric cryptography—the server only stores public keys, which are useless to attackers.
2. No Replay Attacks
Each FIDO2 authentication uses a unique challenge-response, making replay attacks impossible. TOTP codes, once intercepted, can be replayed within their validity window.
3. User Presence Verification
FIDO2 authenticators require physical interaction (touching the security key or biometric verification), ensuring the user is actually present during authentication.
4. Resistant to Social Engineering
Because FIDO2 authentication is automatic and cryptographic, users cannot be tricked into manually entering credentials on a fake site.
Real-World Impact
Major technology companies have reported dramatic security improvements after deploying FIDO2:
- Google reported zero account takeovers among employees using security keys
- Microsoft found that security keys blocked 100% of automated bot attacks and bulk phishing attacks
- The U.S. government has mandated phishing-resistant MFA for federal agencies, with FIDO2 as the recommended standard
Conclusion
While TOTP provides security improvements over passwords alone, it remains vulnerable to sophisticated phishing attacks like those enabled by Evilginx. FIDO2's cryptographic origin binding makes phishing functionally impossible—an attacker cannot relay or reuse FIDO2 credentials because they are cryptographically bound to specific domains.
As phishing attacks grow more sophisticated, organizations should transition to FIDO2-based authentication. The technology is mature, widely supported, and provides phishing-resistant security that TOTP simply cannot match.
Recommendations
- For Organizations: Implement FIDO2/WebAuthn for all user accounts, starting with high-privilege accounts
- For Users: Adopt hardware security keys (Token2 or any other FIDO-certified device) or use platform authenticators (Windows Hello, Touch ID)
- For Developers: Integrate WebAuthn APIs into your applications and educate users about passwordless authentication
- Transition Strategy: Support both TOTP and FIDO2 during migration, but encourage and incentivize FIDO2 adoption
The future of authentication is phishing-resistant, and FIDO2 is leading the way.
See also: A detailed video demonstrating the Evilginx attack against M365.
Subscribe to our mailing list
Want to keep up-to-date with the latest Token2 news, projects and events? Join our mailing list!